Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It requires ongoing management to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
While medication and dietary changes play crucial roles in diabetes management, regular exercise and lifestyle modifications are equally important.
In this article, we will explore how exercise and lifestyle changes can help manage diabetes effectively.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact

Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or becomes resistant to insulin’s effects (Type 2 diabetes).
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems. Managing diabetes is crucial to maintain overall health and prevent complications.
The Benefits of Exercise for Diabetes Management
Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for individuals with diabetes. It helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more effectively.
Exercise also helps lower blood sugar levels, reduce body weight, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being.
Incorporating exercise into your diabetes management plan can have significant positive effects on your health.
Types of Exercise for Diabetes

There are three main types of exercise that are beneficial for diabetes management:
Aerobic Exercise: This includes activities that get your heart rate up, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Strength Training: Engaging in strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, helps build muscle mass, improve metabolism, and control blood sugar levels. Include strength training at least twice a week, targeting all major muscle groups.
Also Read: Maintaining a Healthy Weight as You Age: Diet and Exercise Tips
Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Activities like yoga, Pilates, or tai chi can improve flexibility, and balance, and reduce the risk of falls. Incorporate these exercises into your routine to enhance overall physical well-being.
Creating an Exercise Plan
Before starting an exercise routine, consult with your healthcare team to ensure it aligns with your specific needs and capabilities. Consider the following when creating an exercise plan:
Set realistic goals: Start with small, achievable goals and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
Choose activities you enjoy: Find exercises that you genuinely enjoy to make it easier to stick with your routine.
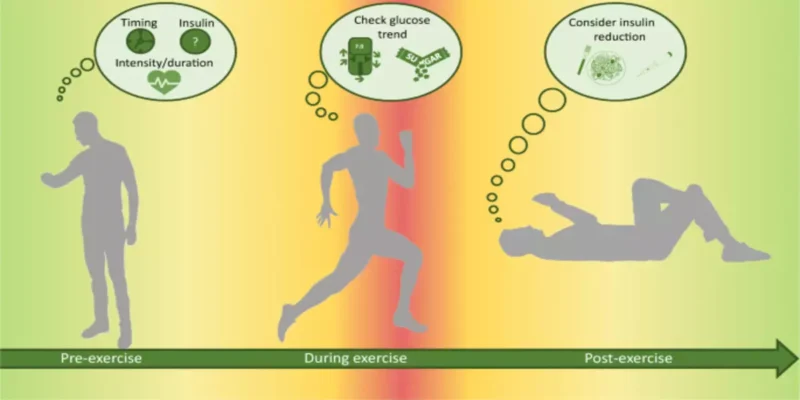
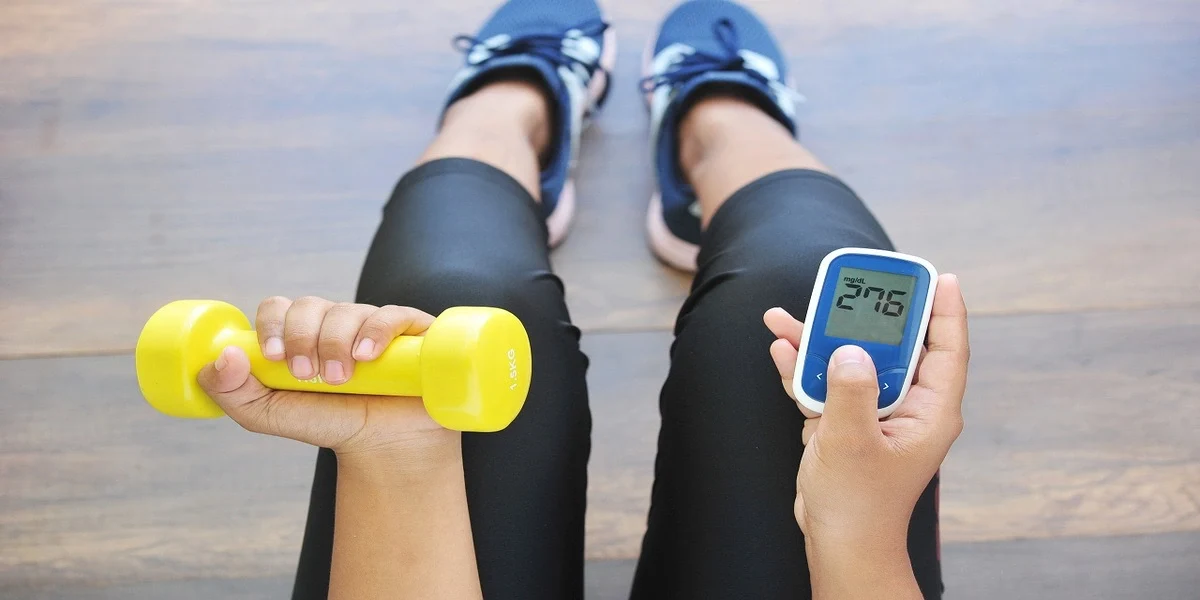
Monitor blood sugar levels: Check your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise to ensure it stays within a safe range.
Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.
Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or unusual symptoms during exercise. If you experience chest pain, dizziness, or extreme fatigue, stop exercising and seek medical attention.
Lifestyle Changes for Diabetes Management

In addition to exercise, certain lifestyle changes can greatly impact diabetes management. Consider the following:
Healthy Eating: Adopt a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit sugary foods, processed snacks, and excessive carbohydrate intake.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare team. This helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar levels.
Managing Stress and Emotional Well-being: Stress can impact blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from loved ones or professionals.
Getting Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can affect blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Maintaining a Supportive Network: Surround yourself with a supportive network of family, friends, or support groups who understand and can provide encouragement on your diabetes management journey.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular exercise and lifestyle changes.
By incorporating exercise into your routine, making healthy food choices, monitoring blood sugar levels, managing stress, getting sufficient sleep, and seeking support, you can improve your overall well-being and successfully manage your diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can exercise alone control diabetes?
Exercise alone may not be sufficient to control diabetes. It should be combined with other lifestyle modifications, such as healthy eating, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, as recommended by your healthcare team.
Q2: How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring may vary depending on individual circumstances and the type of diabetes.
Your healthcare team can provide specific guidelines on how often you should check your blood sugar levels.
Q3: Can I start exercising if I haven’t been physically active for a long time?
If you haven’t been physically active for a while, it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase your activity level. Consult with your healthcare team for guidance on safe exercise routines.
Q4: Are there any specific foods I should avoid as a person with diabetes?
As a person with diabetes, it’s important to limit or avoid foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats. Focus on a balanced diet that includes whole foods, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
Q5: Can exercise help reduce the need for diabetes medication?
Regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle can improve blood sugar control, which may result in a reduction in the need for diabetes medication. However, any adjustments to medication should be made in consultation with your healthcare team.