[ez-toc]
Introduction
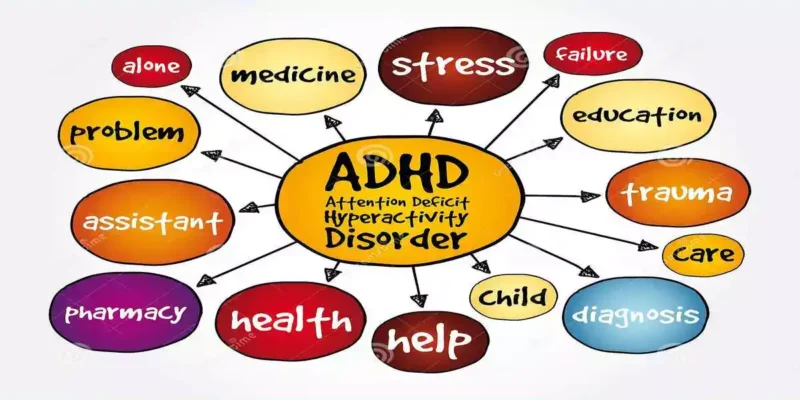
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults, impacting their ability to focus, control impulses, and stay organized.
While ADHD is commonly managed with medication and therapy, research has shown that exercise can also play a significant role in reducing Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder symptoms and improving overall well-being.
In this article, we will explore the relationship between exercise and Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder and how physical activity can be used to manage ADHD symptoms effectively.
Understanding ADHD (Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder) and Its Symptoms
ADHD is characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interferes with daily functioning and development. Symptoms of ADHD may include:
- Inattention
Difficulty paying attention to details, making careless mistakes, and struggling to sustain attention on tasks or activities.
- Hyperactivity
Restlessness, excessive fidgeting, and a constant need to be on the go.
- Impulsivity
Acting without thinking, difficulty waiting turns, and interrupting others.
Benefits of Exercise for Managing ADHD
Engaging in regular physical activity can offer several advantages for individuals with Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder:
- Improved Focus and Attention
Exercise can enhance cognitive function and promote better focus and concentration, helping individuals with Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder stay on task.
- Reduced Hyperactivity
Physical activity can help channel excess energy and reduce hyperactivity in individuals with Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder.
- Enhanced Executive Functioning
Exercise can improve executive functioning skills, such as planning, organization, and time management.
- Mood Regulation
Physical activity triggers the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which can improve mood and reduce irritability often associated with Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder.
Also Read: Exercising for Heart Patients: Cardio Workouts for Improved Quality of Life
Effective Exercises for Managing ADHD
When it comes to managing ADHD symptoms through exercise, the key is to find activities that are enjoyable and engaging. Some effective exercises include:
- Aerobic Activities
Aerobic exercises such as running, cycling, and dancing are beneficial for improving focus and attention.
- Yoga
Yoga combines physical postures with controlled breathing and meditation, promoting relaxation and focus.
- Martial Arts
Martial arts training can help individuals with Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder learn discipline, self-control, and concentration.
- Team Sports
Team sports like soccer, basketball, or volleyball can provide structure, social interaction, and an outlet for excess energy.
- Swimming
Swimming is a low-impact exercise that can be both calming and invigorating for individuals with ADHD.
Implementing Exercise for ADHD Management
Here are some strategies to effectively implement exercise for managing ADHD:
- Consistency is Key
Aim for regular exercise, ideally at least several times a week, to experience the full benefits.
- Incorporate Structured Physical Activities
Include structured exercise sessions in daily routines to promote consistency and make it easier to stick with the routine.
- Combine Exercise with Other Activities
Combining exercise with other tasks, such as listening to educational podcasts during walks, can enhance cognitive benefits.
- Encourage Outdoor Activities
Outdoor activities provide a change of scenery and natural stimuli, which can be beneficial for individuals with Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder.
Precautions and Safety Measures
While exercise can be highly beneficial for managing Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder, it is essential to keep the following precautions in mind:
- Consult with Healthcare Providers: Before starting any exercise program, consult with healthcare providers, especially for individuals with medical conditions or physical limitations.
- Avoid Overstimulation: In some cases, certain high-intensity exercises or environments may lead to overstimulation. Pay attention to individual responses and adjust accordingly.
- Combine Exercise with Other Interventions: While exercise is valuable, it should complement other ADHD management strategies, such as medication and therapy.
Conclusion
Exercise is a powerful and effective tool for managing ADHD symptoms and promoting overall well-being. Engaging in regular physical activity can improve focus, reduce hyperactivity, and enhance executive functioning in individuals with ADHD.
Whether it’s aerobic activities, yoga, martial arts, team sports, or swimming, finding enjoyable and engaging exercises is key to maximizing the benefits.
By incorporating exercise into daily routines and combining it with other interventions, individuals with ADHD can experience significant improvements in attention, impulse control, and mood, leading to a more fulfilling and balanced life.